
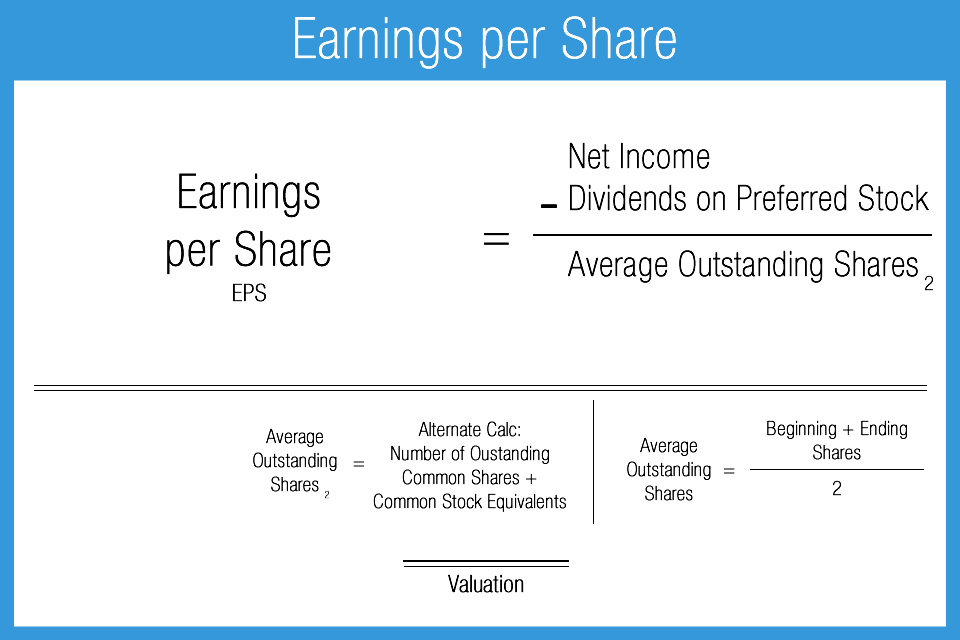
Basic EPS versus diluted EPSĭiluted EPS numbers, unlike the "basic" EPS metric described above, account for all potential shares outstanding. The two most common are the price/earnings (P/E) ratio, which compares a company's stock price to its EPS, and the return on equity (ROE), which indicates how much profit a company generates from its net assets. Share issuances, splits, and stock buybacks all change the denominator by which net income less preferred dividends is divided.ĮPS numbers are most useful when evaluated along with other metrics. A company's net income doesn't accurately reflect its cash flow or the health of its business.Īdditionally, companies can and do manipulate their EPS numbers by changing the number of shares outstanding. Businesses can have much different non-operating expenses, such as tax and interest payments, which affect net income. Non-cash expenses such as depreciation and amortization are subtracted from net income, and the lumpy nature of capital expenditures can cause a company's net income to vary greatly across reporting periods. The main limitation of using EPS to value a stock or company is that EPS is calculated using net income. The company's balance sheet indicates Netflix has not issued any preferred stock, so we don't need to subtract out preferred dividends. For its most recent fiscal year, the company reported a net income of $2,761,395,000 and total shares outstanding of 440,922,000. Let's walk through an example EPS calculation using Netflix ( NASDAQ:NFLX). It's useful to know how to calculate EPS yourself for a few different reasons. Considering a company's earnings as its profit, the company can either distribute that money to shareholders or reinvest it in the company. Preferred dividends must be subtracted because holders of preferred stock have contractual rights to dividend payouts.Ī company reports its EPS in Consolidated Statements of Operations (income statements) in both annual (10-K) and quarterly (10-Q) SEC filings.

Net income is the amount of money that remains in a reporting period after all cash and non-cash expenses are deducted, and net income minus preferred dividends is synonymous with a company's profit for the period.
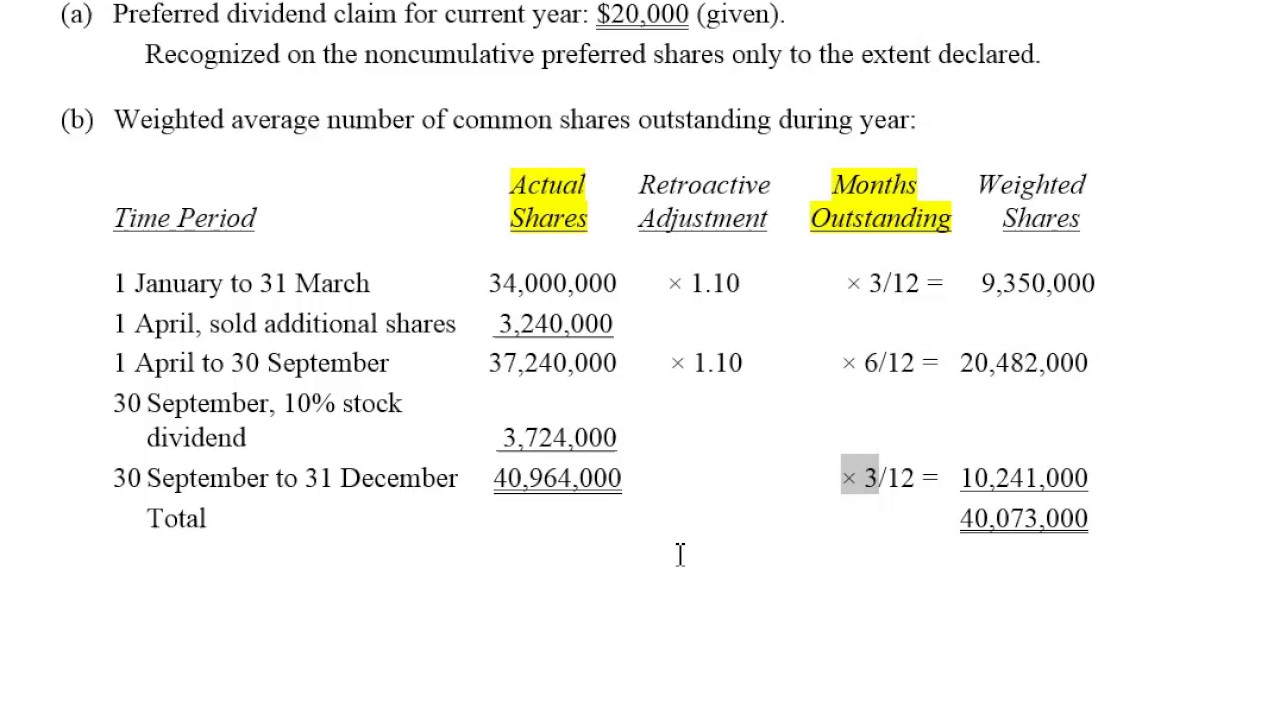
EPS is calculated by subtracting any preferred dividends from a company's net income and dividing that amount by the number of shares outstanding. Mike Price, MSF has ten years of experience value investing.Įarnings per share (EPS) is a metric investors commonly use to value a stock or company because it indicates how profitable a company is on a per-share basis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
